In the rapidly evolving field of biotechnology, cell and gene therapies (CGT) stand out as a beacon of hope for treating a range of previously untreatable conditions. However, the path from discovery to market for these innovative therapies involves regulatory challenges. For businesses operating in this space, understanding, and navigating these hurdles is not just a scientific necessity but a strategic imperative. This blog post delves into the regulatory process for cell and gene therapy, highlighting key steps, challenges, and strategies for success.
The regulatory journey: From concept to cure
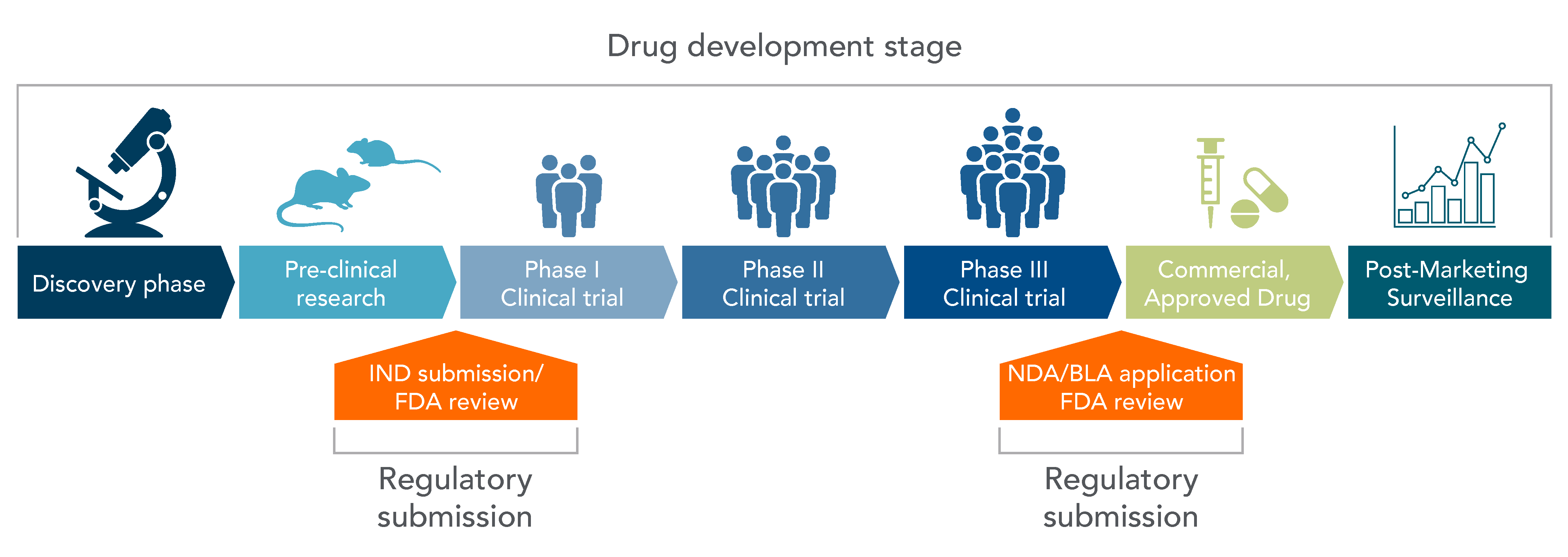
The journey of CGT from the laboratory to the clinic is a meticulous process, segmented into several critical stages (Figure 1) [1].
Step 1 — Discovery Phase: The inception of any CGT product lies in its discovery, where potential therapies are identified and hypothesized for further exploration.
Step 2 — Pre-Investigative New Drug - Preclinical Research: Before any human trials can be conducted, therapies undergo rigorous preclinical research to evaluate safety and efficacy through in vitro and in vivo studies.
Step 3 — IND, Phase 1, Phase 2, and Phase 3 – Clinical Research: Post IND approval, therapies enter a series of clinical trials, each designed to answer specific research questions regarding safety, efficacy, and optimal dosing.
Step 4 — NDA Application – FDA Review: Successful clinical trials lead to the submission of a New Drug Application (NDA) to the FDA, which reviews all submitted data relevant to the drug or device, ultimately deciding on its approval status.
Post Approval — FDA Post-Market Safety & Surveillance: Even after approval, therapies are closely monitored for long‑term safety and efficacy, ensuring ongoing protection for patients.
The statistical reality
The statistical landscape of CGT approvals paints a daunting picture. With only seven out of every 100 therapies making it through the FDA's rigorous review process, the stakes are high. This attrition rate underscores the complexities and uncertainties inherent in developing groundbreaking medical treatments (Figure 2).

Figure 2. Drug Approval after each stage of the development process [2].
Guidance and governance: Charting the regulatory waters
To aid in the development and approval of CGT products, several regulatory and standard-setting bodies have issued guidance documents. The FDA, EMA, ICH, European Pharmacopeia, and USP have all contributed to the regulatory framework, providing developers with critical insights and parameters for CGT development. Since 1998, the issuance of these documents has evolved, reflecting the rapid advancements and growing understanding of CGT.
Since the landmark issuance of the Final Guidance for Human Somatic Cell Therapy and Gene Therapy in March 1998, the FDA has actively published a comprehensive suite of 34 guidance documents, spanning both preliminary drafts and finalized versions. The FDA notably released two crucial final guidance documents within the initial five weeks of 2024 alone [3], highlighting its commitment to facilitating the development and regulatory compliance of cell and gene therapies.
On the international front, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has been instrumental in shaping the regulatory landscape, with 56 guidance documents issued since 2003 [4,5]. This initiative underscores the EMA’s dedication to fostering innovation while ensuring patient safety in the growing field of cell and gene therapy.
Complementing these efforts, the International Council of Harmonization (ICH) has made significant contributions by issuing 20 monographs since 1995 [4], aimed at harmonizing global regulatory standards. The European Pharmacopeia has added 12 monographs from 2014 onwards (Volume 7), providing critical specifications and standards for the industry [4]. The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) has also been pivotal, with 7 monographs dedicated to cell and gene therapies [3], underscoring the specialized focus required to navigate this complex domain.
The ongoing issuance of guidance and monographs by these regulatory and standard-setting bodies is a testament to the evolving nature of cell and gene therapies. As the industry continues to advance, it is expected that additional regulatory guidance will be necessary to address emerging challenges and opportunities, ensuring that these innovative therapies are developed and delivered to patients with the highest standards of safety and efficacy.
The role of strategic partnerships: Leveraging expertise for success
Given the intricate and evolving regulatory environment, CGT developers are advised to seek specialized guidance. Strategic partnerships with entities experienced in navigating the regulatory landscape, such as Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT), can be invaluable. These partners offer expertise from the pre-clinical stages through IND submission and beyond, providing a roadmap for successful navigation through the regulatory process.
For businesses in the CGT domain, understanding the regulatory landscape is not merely a compliance requirement but a strategic advantage. The complexities of CGT development demand a proactive approach, where regulatory challenges are anticipated and addressed with precision and expertise. By strategic partnerships with IDT and leveraging the wealth of guidance available, CGT developers can navigate the regulatory maze more effectively, bringing life-changing therapies from concept to cure with greater efficiency and success. Contact us today for a free consultation on your CRISPR therapeutic development project and discover how our expertise can help you achieve your goals.

